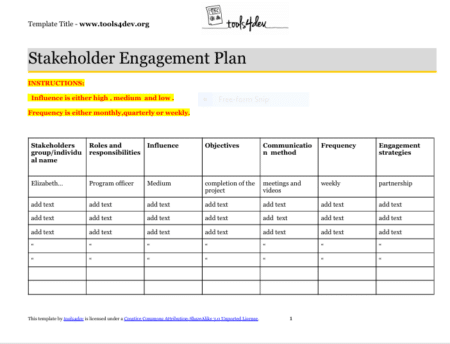
This is a structured document that analyses stakeholders influence and interest to ensure their input is secured. In essence, an organization plans on this to still have the best relationships with the other parties. Operating without a stakeholder’s engagement plan is like gambling with the organizations success and can lead to significant problems which may include;
- Miscommunication and misaligned
Miscommunications can erode trust and lead to conflicts
- Missed requirements and poor solutions
Without any engagement , stakeholders may feel excluded ,leading to resistant and may voice unexpected . III. Increased costs and delays Problems arising from poor engagements often lead to consuming massive amount of time , funds and management focus .
- Damaged license to operate
Some projects have legal requirements for stakeholder consultant . Failing to meet these obligations can result to legal actions or fines .
- Talent and relation issues
Professionals are hesitant to join or stay with an organization known for chaotic management and constant controversy. Examples of organisations that failed due to lack of effective stake holder engagement planning ;
In many low-resource settings, governments and NGOs have invested heavily in water supply and sanitation (WASH) systems such as boreholes, water tanks, taps, pipes, and toilets. Despite these investments, a significant number of these systems have failed to deliver the expected outcomes. Across many regions, non-functional WASH infrastructure remains visible long after project completion, highlighting systemic challenges in planning and sustainability. Studies and monitoring efforts have shown that 30–40% of water supply systems are non-functional. Between 1990 and 2010, these failures represented an estimated USD 1.2–1.5 billion in lost investments. These losses affect not only donors and governments but also communities that continue to lack reliable access to safe water and sanitation. The main factors contributing to WASH system failure include:
- Poor project planning
- Inappropriate technology choices that do not match local context
- Limited stakeholder and community involvement during planning and implementation
- Lack of maintenance systems and post-project support
- Weak accountability mechanisms for long-term performance
- Insufficient demand creation for sanitation services
- Over-emphasis on infrastructure while neglecting hygiene behavior change
This case demonstrates that WASH challenges are not purely technical or engineering problems. Sustainable water and sanitation systems require:
- Strong community ownership and engagement
- Context-appropriate technologies
- Ongoing monitoring and maintenance plans
- Clear roles and accountability after project completion
- Integration of behavior change and demand creation, not just infrastructure delivery
The failure of WASH systems underscores the importance of sustainability planning, stakeholder engagement, and accountability in development projects. Without these elements, even well-funded and technically sound projects risk becoming abandoned assets rather than lasting solutions. Successful WASH projects depend not only on building infrastructure, but on people, processes, and long-term commitment. Ignoring these factors leads to wasted resources and unmet community needs.
Non-governmental organizations play a critical role in supporting vulnerable populations, yet many NGO projects struggle to remain sustainable after donor funding ends. Studies indicate that only about 10% of NGO projects achieve their intended long-term outcomes. In Dadaab Refugee Camp, Kenya, the sustainability of World Food Programme (WFP) projects has consistently fallen short of stakeholder expectations, affecting both program effectiveness and satisfaction. This study examined how stakeholder participation across the project life cycle influences the sustainability of WFP projects in Dadaab Refugee Camp. Specifically, it assessed stakeholder involvement during:
- Project conceptualization
- Project planning
- Project implementation
- Project monitoring
A descriptive research design was used. Data were collected from individuals directly and indirectly involved in WFP project implementation at Dadaab. Out of 133 distributed questionnaires, 87 valid responses were analyzed using SPSS (version 20). Correlation analysis was used to measure the relationship between stakeholder participation and project sustainability. The study found a positive relationship between stakeholder participation and project sustainability:
- Project conceptualization: Strong positive correlation (r = 0.645)
- Project planning: Strong positive correlation (r = 0.674)
- Project implementation: Weak positive correlation (r = 0.437)
- Project monitoring: Strong positive correlation (r = 0.666)
These findings show that early and ongoing stakeholder involvement—especially during conceptualization, planning, and monitoring—has a significant impact on project sustainability. The study concludes that active and continuous stakeholder participation throughout all project phases is a practical and effective strategy for improving project sustainability. Projects that engage stakeholders from the beginning are more likely to achieve better outcomes and remain operational beyond donor support. For NGOs such as the World Food Programme, stakeholder participation is not optional—it is essential. Sustainable projects require a holistic approach that integrates all stakeholders from project initiation through monitoring and evaluation. These case studies clearly demonstrate that stakeholder engagement is a critical determinant of project success and sustainability. Whether in infrastructure development or humanitarian programming, failure to involve stakeholders meaningfully leads to wasted resources, unmet community needs, and project collapse. A well-designed stakeholder engagement plan helps align expectations, improve accountability, reduce risks, and ensure long-term impact. Organizations that prioritize inclusive participation throughout the project life cycle are far more likely to deliver sustainable and successful outcomes. Below is sample template for the plan ;